Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the joints, causing pain, inflammation, and stiffness. While the exact cause of RA is still unknown, there is growing evidence suggesting a strong genetic component in its development. Understanding the genetic factors behind RA is crucial for advancements in prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. This blog will explore the genetic basis of RA, the role of environmental factors in its development, and debunk common myths surrounding the condition. Additionally, we will discuss the potential implications of genetic testing in predicting and managing RA. By taking a multifactorial approach to understanding RA, healthcare professionals can better support individuals with a genetic predisposition to this debilitating condition.
Background on rheumatoid arthritis (RA)

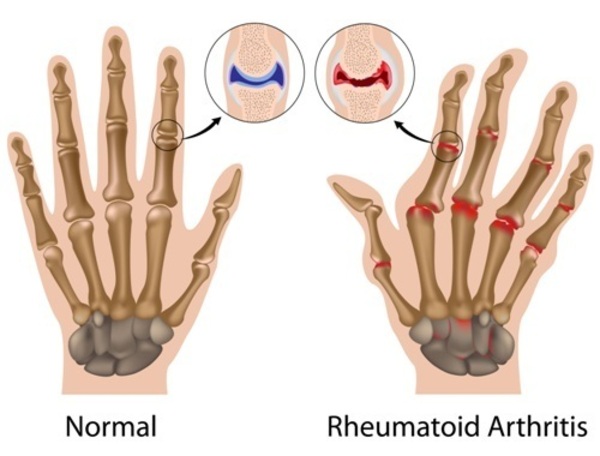
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the joints, causing pain, inflammation, and stiffness. It is characterized by the immune system mistakenly attacking the synovial lining of the joints, leading to joint damage and deformity over time. RA can affect various joints, including those in the hands, feet, wrists, and knees.
RA affects approximately 1% of the global population and is more prevalent in women than men. The exact cause of RA is still unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Understanding the underlying genetic basis of RA is crucial for advancements in prevention, diagnosis, and treatment strategies for this debilitating condition.
Importance of understanding the genetic factors in RA
Understanding the genetic factors associated with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is of utmost importance for several reasons. Firstly, it helps in identifying individuals who may be at a higher risk of developing the disease. This knowledge can enable early intervention and preventive measures, improving disease outcomes. Secondly, studying the genetic basis of RA provides insights into the underlying mechanisms and pathways involved in the disease. This contributes to the development of targeted therapies that can specifically address these pathways, leading to more effective treatments. Additionally, understanding the genetic factors allows for the identification of potential biomarkers for predicting disease progression and response to treatment. Ultimately, unraveling the genetic component of RA offers hope for personalized medicine approaches and improved management of this debilitating condition.
Understanding the Genetic Component

The genetic component of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) plays a significant role in the development and progression of the disease. Researchers have identified several genetic factors that contribute to the susceptibility of RA. These genetic variants are involved in immune dysregulation and inflammation, which are key features of RA.
Studies have shown that specific genetic variants, such as the HLA-DRB1 gene, are associated with an increased risk of developing RA. Other genes, such as PTPN22 and CTLA4, have also been implicated in RA susceptibility.
However, it is important to note that genetics alone do not determine the development of RA. Environmental factors, such as smoking, infections, and hormonal changes, also interact with genetic factors to influence the risk of developing RA. Hence, understanding the genetic component of RA is crucial, as it provides insights into the underlying mechanisms and opens avenues for personalized medicine approaches in the prevention and treatment of this debilitating condition.
Genetic basis of rheumatoid arthritis

Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has a strong genetic component. The genetic basis of RA lies in the interaction between specific genes and the immune system. Researchers have identified several genes involved in immune regulation and inflammation that contribute to the development of RA. The most well-known genetic variant associated with RA is the HLA-DRB1 gene. This gene plays a crucial role in presenting antigens to immune cells, leading to an abnormal immune response in individuals with RA. Additional genetic variants, such as PTPN22 and CTLA4, have also been implicated in RA susceptibility. These genetic factors contribute to the dysregulation of the immune system and the chronic inflammation observed in RA. Understanding the genetic basis of RA is essential for developing targeted therapies and personalized treatment approaches.
Genetic variants associated with increased susceptibility to RA
Several genetic variants have been identified that are associated with an increased susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The most well-known genetic variant is the HLA-DRB1 gene, which is involved in immune regulation and presenting antigens to immune cells. This variant increases the risk of developing RA by triggering an abnormal immune response. Other genetic variants, such as PTPN22 and CTLA4, have also been implicated in RA susceptibility. These variants play a role in immune system regulation and contribute to the dysregulation of the immune response observed in RA. Understanding the specific genetic variants associated with RA can help in early detection, risk assessment, and the development of targeted therapies.
The Role of Environmental Factors
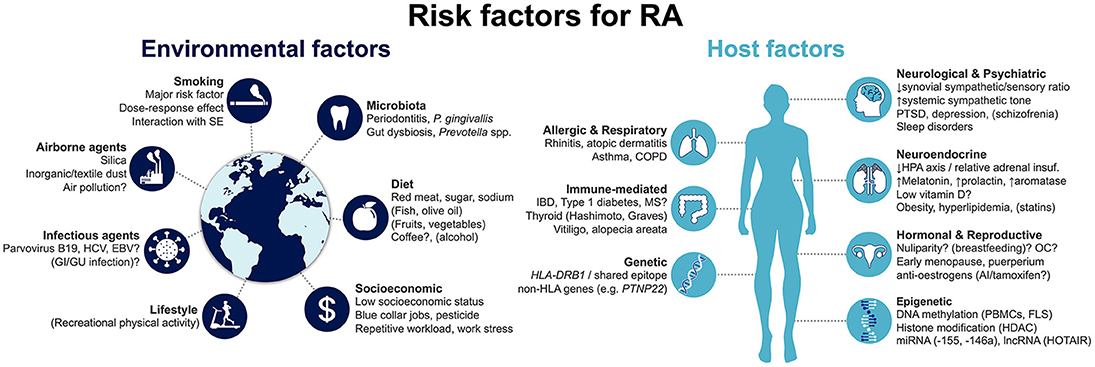
Environmental factors also play a crucial role in the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Exposure to certain environmental triggers can activate the immune system and potentially trigger the onset of the disease in individuals who are genetically predisposed. Factors such as smoking, infections, hormonal changes, and exposure to pollutants have been linked to an increased risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. These external influences interact with genetic susceptibility to create an environment that promotes the development of the disease. The relationship between genetics and the environment is complex, and further research is needed to fully understand how these factors interact and contribute to the development and progression of rheumatoid arthritis. Understanding the role of environmental factors can help in implementing preventive strategies and lifestyle modifications to reduce the risk of developing this chronic and debilitating condition.
Influence of environmental factors on the development of RA

Environmental factors play a significant role in the development of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Various external factors can trigger the immune system and potentially activate the onset of the disease in individuals who are genetically predisposed. Smoking, infections, hormonal changes, and exposure to pollutants have been linked to an increased risk of developing RA. These environmental triggers interact with genetic susceptibility, creating an environment that promotes the development of the disease. However, it is important to note that not everyone exposed to these factors will develop RA. The exact mechanisms through which these environmental factors influence RA development are still being studied. Understanding the influence of environmental factors is crucial for implementing preventive strategies and lifestyle modifications to reduce the risk of developing this chronic and debilitating condition.
Interaction between genetics and environment in RA
The development of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is influenced by the interaction between genetic factors and environmental triggers. While genetic susceptibility plays a role in determining an individual's predisposition to RA, environmental factors can activate the disease in genetically susceptible individuals. Certain environmental factors, such as smoking, infections, hormonal changes, and exposure to pollutants, have been found to increase the risk of developing RA. These factors can trigger the immune system, leading to the onset of the disease. It is important to note that not everyone with a genetic predisposition and exposure to environmental triggers will develop RA. The complex interaction between genetics and the environment highlights the multifactorial nature of the disease and emphasizes the need for a comprehensive approach to understanding and managing RA.
Debunking the Myths

Myth: Rheumatoid arthritis is solely caused by genetics
Contrary to popular belief, rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is not solely caused by genetics. While genetic factors play a significant role in determining an individual's predisposition to the disease, they are not the sole cause. Environmental factors also play a crucial role in triggering RA in genetically susceptible individuals. Smoking, infections, hormonal changes, and exposure to pollutants are some of the environmental factors that can increase the risk of developing RA. This highlights the importance of a multifactorial approach in understanding the disease. It is essential to consider both genetic and environmental factors to better comprehend the development and progression of RA and develop effective preventive and treatment strategies.
Myth: Everyone with a family history of RA will develop the disease
Another myth surrounding RA is that everyone with a family history of the disease will inevitably develop it. While having a family history of RA increases the risk of developing the disease, it does not guarantee its occurrence. The interplay between genetic susceptibility and environmental triggers is complex, and not all individuals with a genetic predisposition will develop RA. Other factors, such as lifestyle choices, overall health, and the presence of additional risk factors, can also influence the development of the disease. It is crucial for individuals with a family history of RA to be aware of their increased risk but understand that preventive measures and early intervention can help manage and reduce the impact of the disease.
Myth: Rheumatoid arthritis is solely caused by genetics
Contrary to popular belief, rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is not solely caused by genetics. While genetic factors play a significant role in determining an individual's predisposition to the disease, they are not the sole cause. Environmental factors also play a crucial role in triggering RA in genetically susceptible individuals. Smoking, infections, hormonal changes, and exposure to pollutants are some of the environmental factors that can increase the risk of developing RA. This highlights the importance of a multifactorial approach in understanding the disease. It is essential to consider both genetic and environmental factors to better comprehend the development and progression of RA and develop effective preventive and treatment strategies.
Myth: Everyone with a family history of RA will develop the disease
Contrary to the myth, having a family history of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) does not guarantee that an individual will develop the disease. While having a close relative with RA does increase the risk, it does not mean that everyone with a family history will inevitably develop the condition. Numerous studies have shown that the overall risk of developing RA in the general population is relatively low, even for individuals with a family history. It is important to recognize that genetic factors are just one piece of the puzzle, and environmental triggers also play a significant role in the development of RA. Therefore, it is essential not to assume that a family history of RA guarantees the onset of the disease, but rather to focus on understanding and managing the risk factors associated with it.
Genetic Testing and Predictive Medicine

Genetic testing has emerged as a promising tool for risk assessment in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). By analyzing an individual's DNA, genetic testing can identify specific genetic variants associated with an increased risk of developing RA. This information can help individuals understand their genetic predisposition and make informed decisions about their health.
Moreover, genetic testing holds implications for predictive medicine in RA. By identifying individuals who are at higher risk, healthcare providers can implement personalized prevention strategies to mitigate the impact of environmental triggers and potentially delay or prevent the onset of the disease. Additionally, genetic testing can help guide treatment decisions, as it can provide insights into an individual's response to specific medications, allowing for more targeted and effective treatment plans.
However, it is important to note that genetic testing is just one piece of the puzzle in understanding and managing RA. A multifactorial approach that takes into account both genetic and environmental factors is crucial for comprehensive care.
Genetic testing for rheumatoid arthritis risk assessment

Genetic testing has emerged as a valuable tool for risk assessment in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). By analyzing an individual's DNA, genetic testing can identify specific genetic variants associated with an increased risk of developing RA. This information can help individuals understand their genetic predisposition to the disease and make informed decisions about their health.
Genetic testing can also provide important insights into an individual's response to specific medications, allowing for more targeted and effective treatment plans. This personalized approach can lead to better outcomes and improved quality of life for individuals with RA. Furthermore, by identifying individuals who are at higher risk, healthcare providers can implement personalized prevention strategies to mitigate the impact of environmental triggers and potentially delay or prevent the onset of the disease. However, it is important to remember that genetic testing is just one piece of the puzzle in understanding and managing RA, and a comprehensive approach that considers both genetic and environmental factors is essential.
Implications of genetic testing in the prevention and treatment of RA

Genetic testing for rheumatoid arthritis holds significant implications for both prevention and treatment strategies. By identifying specific genetic variants associated with an increased risk of RA, healthcare providers can implement personalized prevention strategies. These may include lifestyle modifications and targeted interventions to mitigate the impact of environmental triggers. Additionally, genetic testing can provide valuable information on an individual's response to specific medications. This allows for more targeted and personalized treatment plans, improving the efficacy and outcomes of RA management. Moreover, genetic testing can aid in early detection of the disease, providing an opportunity for early intervention and better disease control. However, it is crucial to note that genetic testing is just one tool, and a comprehensive approach considering both genetic and environmental factors is essential for effective RA prevention and treatment.
Conclusion

In conclusion, understanding the genetic component of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. While genetics play a significant role in RA, it is important to debunk the myths that suggest it is solely caused by genetics or that everyone with a family history will develop the disease. The interaction between genetics and environmental factors is key to the development of RA. Genetic testing offers a promising approach to assess an individual's risk and tailor personalized prevention and treatment plans. However, it is important to adopt a multifactorial approach that considers both genetic and environmental factors to fully understand and manage RA. By doing so, healthcare providers can improve outcomes and enhance the quality of life for individuals with RA.
Summary of key points

In summary, there are key points to consider when discussing the genetic component of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). While genetics play a significant role in RA, it is important to debunk the myths that suggest it is solely caused by genetics or that everyone with a family history will develop the disease. The interaction between genetics and environmental factors is key to the development of RA. Genetic testing offers a promising approach to assess an individual's risk and tailor personalized prevention and treatment plans. However, it is important to adopt a multifactorial approach that considers both genetic and environmental factors to fully understand and manage RA. By doing so, healthcare providers can improve outcomes and enhance the quality of life for individuals with RA.
The importance of a multifactorial approach in understanding and managing RA

A multifactorial approach is crucial in understanding and managing rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This approach recognizes the complex interplay between genetic factors, environmental triggers, and individual lifestyle choices. By considering all these factors, healthcare providers can develop personalized prevention and treatment plans that optimize outcomes for patients with RA.
A multifactorial approach allows for a more comprehensive assessment of an individual's risk for developing RA and helps identify potential strategies for reducing disease progression and improving quality of life. Additionally, this approach emphasizes the importance of lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise, and managing stress, which can significantly impact disease management and symptom control. By adopting a multifactorial approach, healthcare providers can empower patients to take an active role in their care and improve long-term outcomes for individuals living with RA.

.jpg)