Introduction:
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks the joints, causing chronic inflammation, pain, and stiffness. It is a chronic, progressive condition that can cause joint deformities and disabilities. RA can occur at any age, but it most commonly affects people in their middle age.

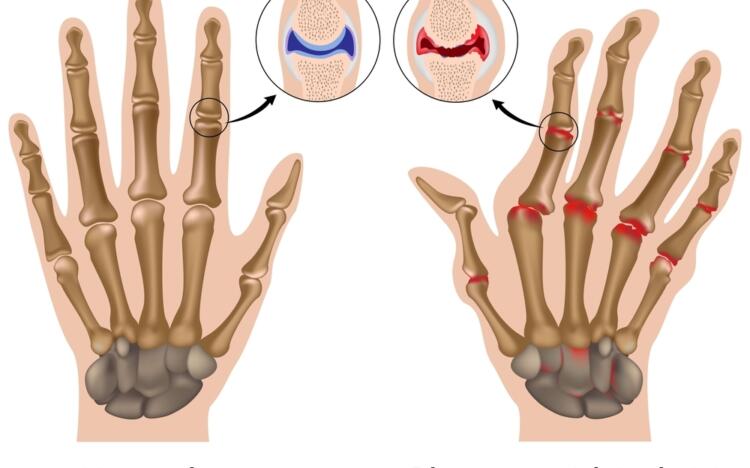
RA is a chronic autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system attacks the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and damage. The exact cause of RA is not known, but it is believed to be triggered by a combination of genes and environmental factors. The inflammation caused by RA can damage the lining of the joints and cause bone erosion and deformities over time. RA can also affect other organs, such as the eyes, lungs, and heart.
Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis:
The symptoms of RA can vary from person to person, but the most common symptoms include joint pain, swelling, and stiffness, especially in the morning or after sitting for long periods. Other symptoms may include fatigue, fever, weight loss, and a general feeling of being unwell. RA can affect any joint in the body, but it most commonly affects the small joints in the hands and feet. In some cases, RA can cause joint deformities and make it difficult to perform everyday tasks like dressing and holding objects.
There are several treatment options available for RA, including medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes. It is important to seek medical treatment for RA as early as possible to prevent joint damage and disability. However, there is currently no cure for RA, and it is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management and treatment.
Understanding Bone and Joint Inflammation: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Hip replacement: A surgical procedure that involves replacing a damaged hip joint with an artificial one
Promising Research and Developments for Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatments
Rheumatoid Arthritis in Children: Signs, Symptoms, and Treatment
Overcoming Fatigue and Depression Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis
The Relationship Between Diet and Rheumatoid Arthritis Management
When to Seek Medical Help for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Key Differences Between Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis
Living with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Coping Strategies and Treatment Options
Understanding the Symptoms and Causes of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Early diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and stiffness. The exact cause of RA is not known, but it is believed to be triggered by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. RA can occur at any age, but it most commonly affects people in their middle age.
When to Seek Medical Help for Rheumatoid Arthritis
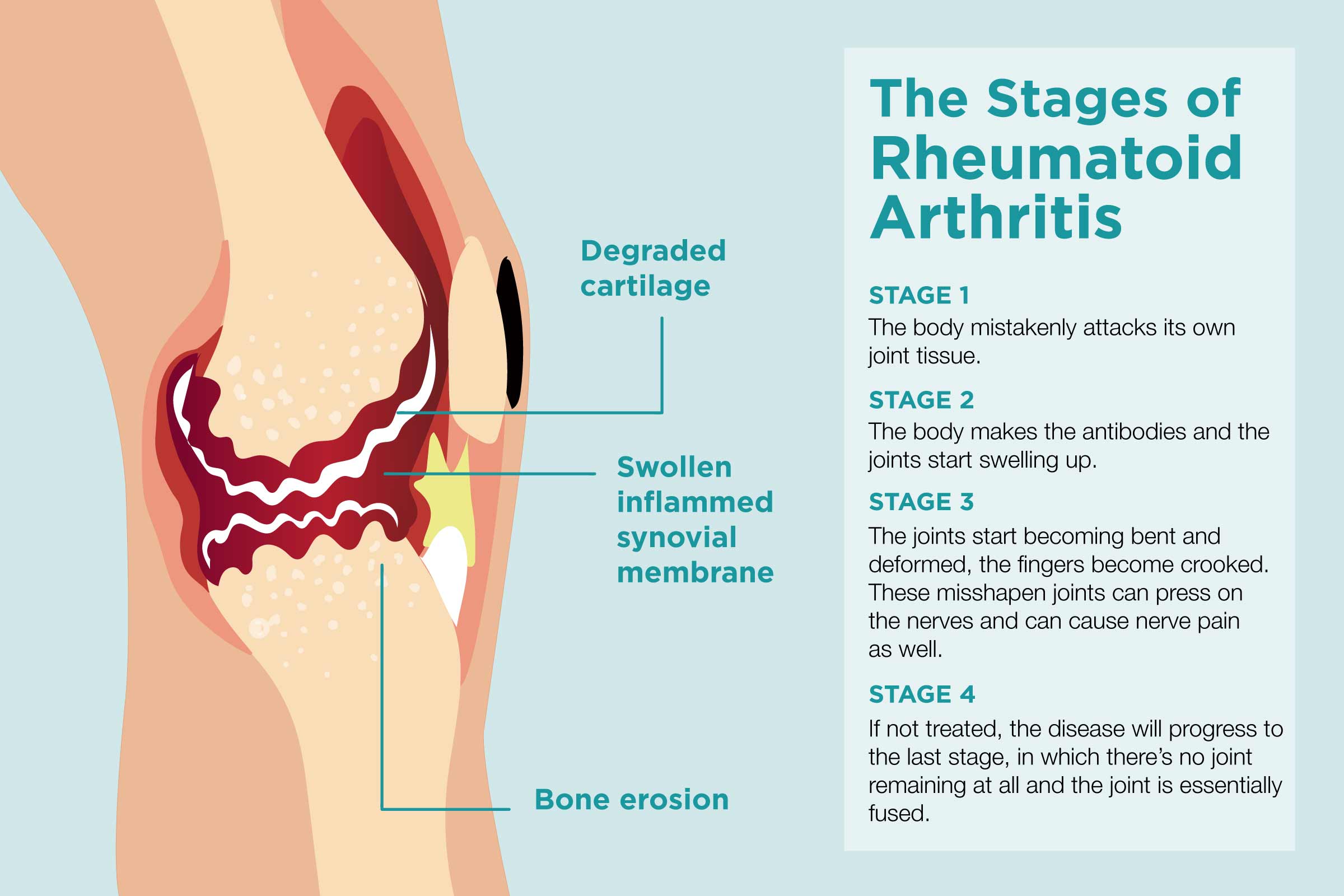
It is important to seek medical help if one experiences joint pain, swelling, and stiffness that lasts for more than two weeks, as these could be the early signs of RA. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in managing RA and preventing joint damage and disability. A person should also seek medical help if they notice other symptoms such as fatigue, fever, and weight loss, which are common in people with RA.
Tests for Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnosis
To be diagnosed with RA, a medical professional may perform several tests, including blood tests, imaging tests, and joint fluid analysis. Blood tests can detect the presence of antibodies that are common in people with RA, while imaging tests, such as X-rays or ultrasound, can show joint damage or inflammation. Joint fluid analysis involves removing a small amount of fluid from the affected joint and analyzing it for signs of RA.
In conclusion, early diagnosis and treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis are essential in managing the disease and preventing joint damage and disability. If one experiences joint pain or other symptoms associated with RA, they should seek medical help to determine the cause and begin a treatment plan.

Understanding Treatment for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes inflammation, pain, and stiffness in joints. It can occur at any age but is most commonly seen in people in middle age. Early diagnosis of RA is essential in managing the disease and preventing joint damage and disability. Seeking medical assistance is crucial if one experiences joint pain, swelling, and stiffness that lasts more than two weeks. Other symptoms like fatigue, fever, and weight loss should also be taken seriously.
Medications and Therapy for RA
There are various treatment options available for RA, including medications and therapy. The doctor will recommend a treatment plan based on the severity of the disease and the patient's medical history. Common medications used to manage RA symptoms include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) – pain relievers that reduce inflammation.
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) – slow the progression of RA.
- Biologic drugs – target specific parts of the immune system that cause inflammation.
Apart from medication, physical therapy may be recommended to improve flexibility, strength, and range of motion in the affected joints. Occupational therapy may also be necessary to help with daily activities such as dressing and bathing. In severe cases, surgery may be required.
Tests like blood tests, imaging tests, and joint fluid analysis are performed to diagnose RA. Blood tests detect the presence of antibodies common in people with RA. Imaging tests, like X-rays or ultrasound, show joint damage or inflammation. Joint fluid analysis involves examining a small sample of fluid removed from the affected joint.
Early diagnosis and prompt treatment of RA can prevent joint damage and disability. Understanding the available treatment options is essential in managing the disease and living as comfortably as possible.
Seeking Medical Help for Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain and Inflammation
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease that causes joint inflammation, pain, and stiffness. It is more common in middle-aged individuals but can occur at any age, and early diagnosis is crucial in managing the disease and preventing joint damage and disability. If an individual experiences joint pain, swelling, and stiffness that lasts more than two weeks, seeking medical assistance is necessary. Other symptoms like fatigue, fever, and weight loss should not be ignored as well.
Joint swelling and stiffness
Tests like blood tests, imaging tests, and joint fluid analysis are performed to diagnose RA. Blood tests detect the presence of antibodies commonly found in people with RA. Imaging tests such as X-rays or ultrasound show joint damage or inflammation. Joint fluid analysis involves examining a small sample of fluid removed from the affected joint.
Rheumatoid nodules
There are various treatment options available for RA, including medications and therapy. The treatment plan recommended by the doctor will depend on the severity of the disease and the person's medical history. Common medications used to manage RA symptoms include Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and Biologic drugs that target specific parts of the immune system that cause inflammation. Physical therapy may also be recommended to improve flexibility, strength, and range of motion in the affected joints, while occupational therapy may help with daily activities like dressing and bathing. In severe cases, surgery may be required.
Understanding the available treatment options is essential in managing RA and living as comfortably as possible. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment can prevent joint damage and disability, so it is crucial to seek medical help if you experience any RA symptoms.
Complications of Rheumatoid Arthritis
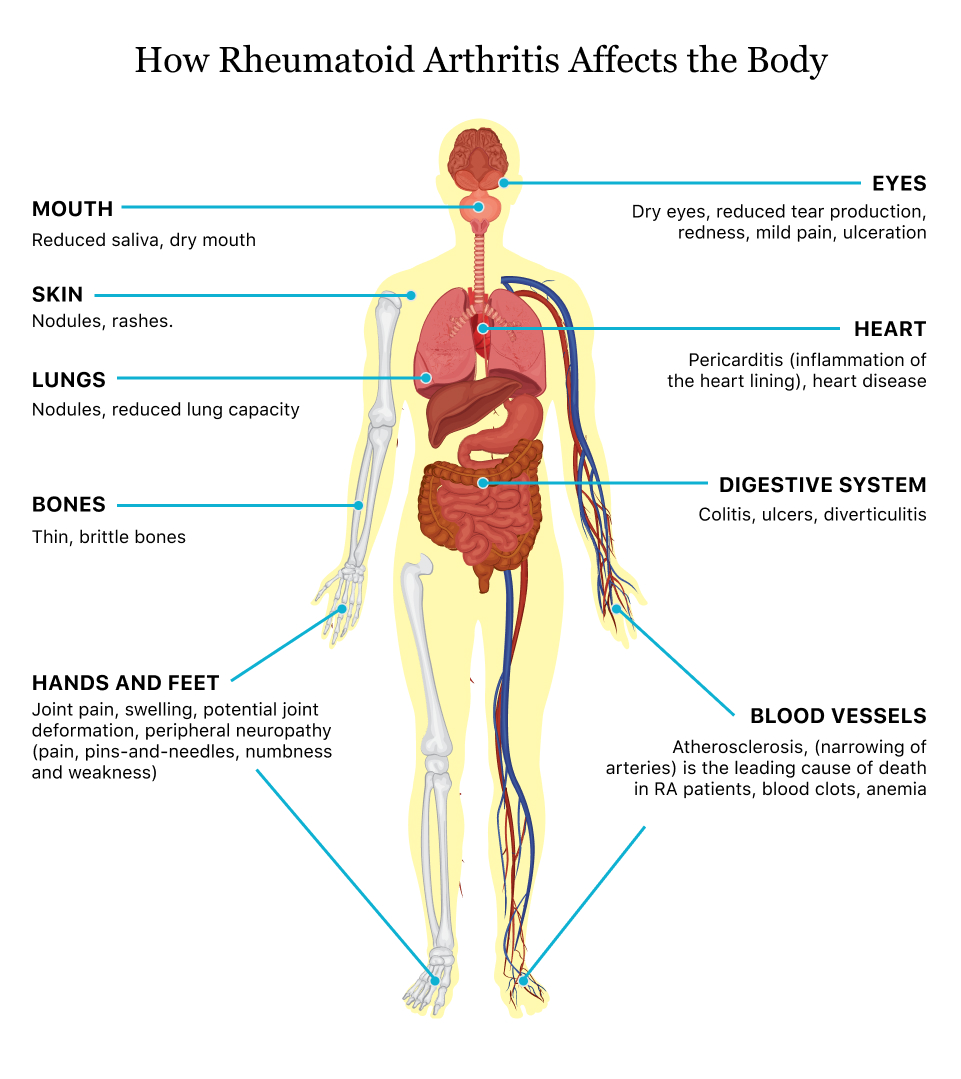
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) can cause a variety of complications that affect joints, as well as other parts of the body. Understanding these risks is an essential part of managing the disease and preventing long-term damage and disability.
Heart and Lung effects
RA increases the risk of heart disease and stroke, which can be life-threatening. The inflammation caused by RA can also lead to lung problems like pleurisy, which is inflammation of the lining around lungs, and interstitial lung disease, which causes scarring of lung tissue. RA patients are more likely to develop infections like pneumonia and are also at higher risk for blood clots.
Eye problems
RA can also affect the eyes and lead to various conditions like dry eye syndrome, scleritis, and uveitis. Scleritis is inflammation of the white part of the eye, while uveitis affects the middle layer of the eye. If left untreated, these conditions can cause vision loss.
Treating RA promptly and effectively can prevent these complications and improve quality of life. Regular monitoring and follow-up with a healthcare provider are necessary to catch any potential issues early and provide appropriate treatment.

Talking with a Rheumatologist
For individuals with rheumatoid arthritis, speaking with a rheumatologist is an essential part of managing the disease effectively. Rheumatologists are specialists who focus on diagnosing and treating arthritis and related conditions. They can provide valuable guidance on the best treatment options, lifestyle changes, and preventive measures.
Preparing for a Doctor's Appointment
Before the appointment with a rheumatologist, it is essential to prepare. The following are some practical tips:
- Write down any symptoms or changes - Keeping a journal of symptoms or changes observed can help provide the rheumatologist with important information.
- <b>Make a list of all medicationsb> - Whether prescribed or over-the-counter, list medications taken on a daily or infrequent basis.
By preparing for the appointment, it can help individuals engage in a productive conversation with their rheumatologist, and work towards an effective strategy for managing their arthritis.

