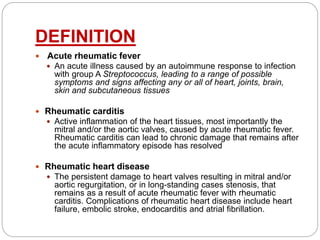
Introduction to Rheumatic Fever

Rheumatic Fever is a rare but serious inflammatory disease that primarily affects the joints, heart, skin, and brain. It typically occurs after an untreated or inadequately treated streptococcal throat infection. Rheumatic Fever can develop in individuals of any age, but it most commonly occurs in children between the ages of 5 and 15. The disease is characterized by symptoms such as joint pain and swelling, fever, rash, and heart murmurs. If left untreated, Rheumatic Fever can lead to long-term complications and damage to the heart valves. Early diagnosis and proper treatment are crucial in managing this condition.
Definition and overview of Rheumatic Fever
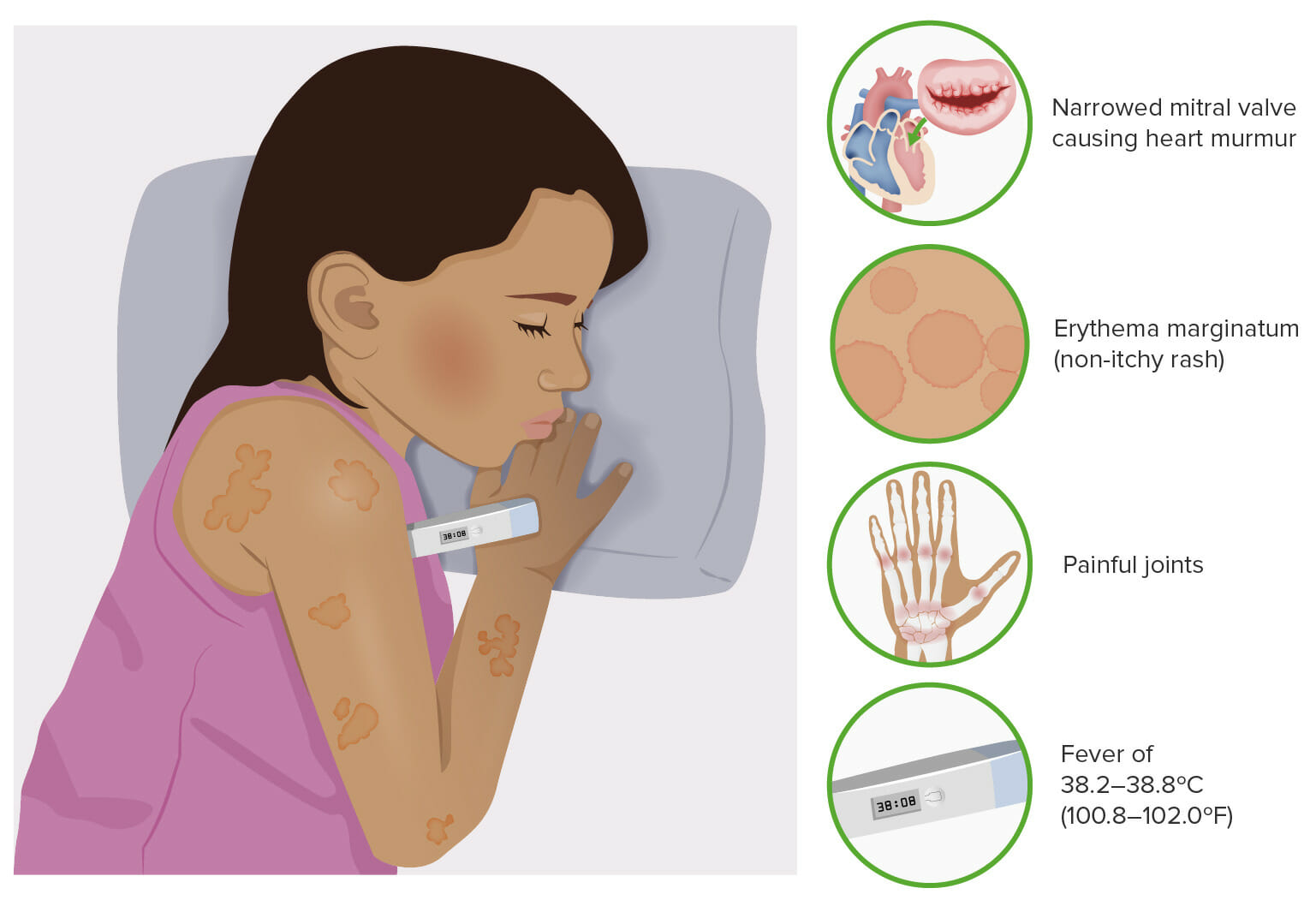
Rheumatic Fever is a systemic inflammatory disease that can develop after a group A Streptococcus infection, such as strep throat or scarlet fever. It primarily affects children aged 5 to 15, although adults can also be affected. Rheumatic Fever primarily targets the heart, joints, skin, and brain. The key characteristic of this condition is its ability to cause damage to the heart valves, leading to rheumatic heart disease. It is important to diagnose and treat Rheumatic Fever promptly to prevent severe complications and long-term health issues.
History and prevalence of Rheumatic Fever
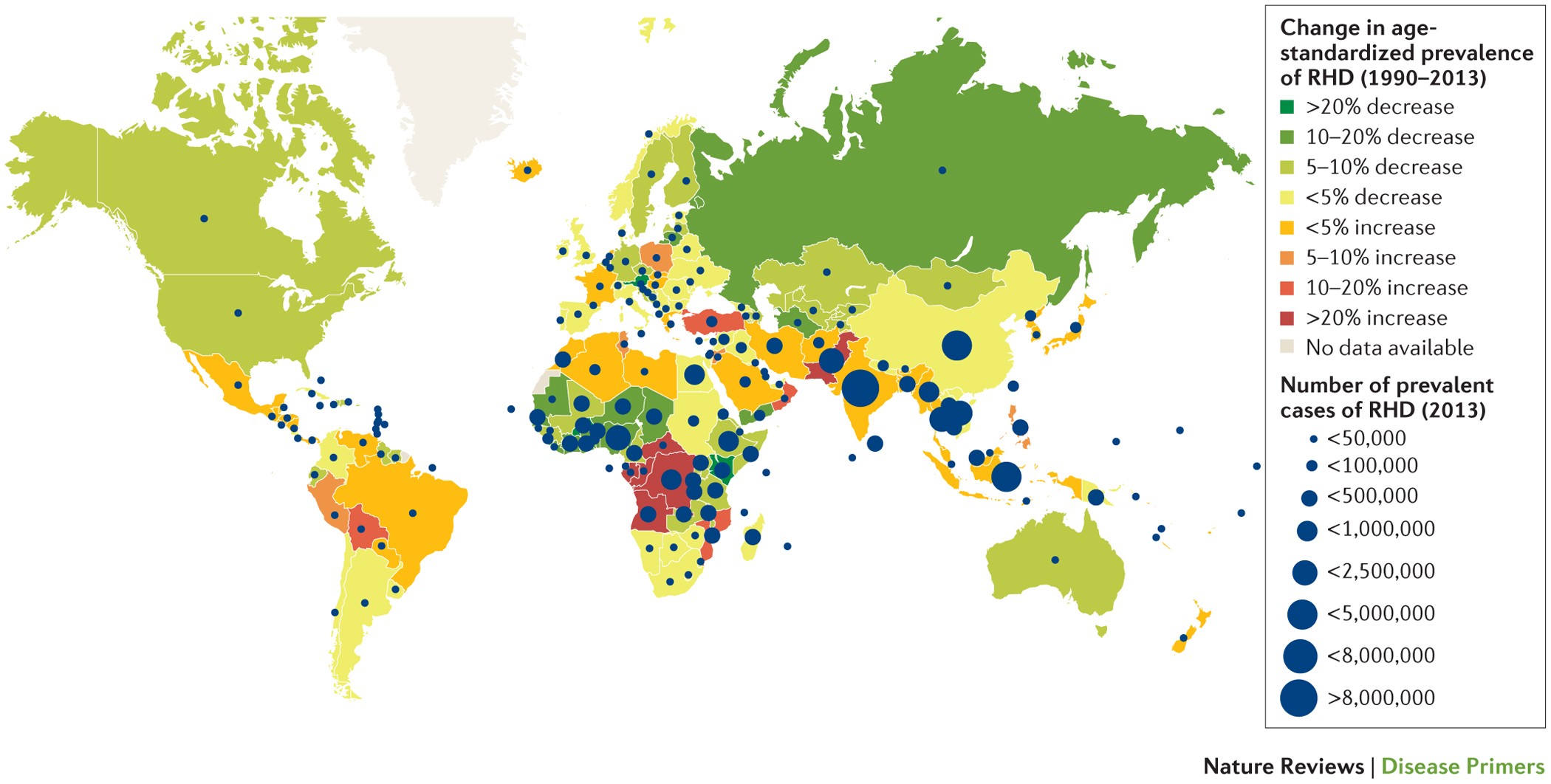
Rheumatic fever is not a new disease and has been recognized for centuries. The first known cases of rheumatic fever were documented in the 15th century. However, it was not until the late 19th century that the link between streptococcal infection and rheumatic fever was established. Since then, the prevalence of rheumatic fever has varied across different regions and populations. In developed countries, the incidence of rheumatic fever has significantly decreased due to improved hygiene and increased access to healthcare. However, in developing countries with limited resources, rheumatic fever remains a significant public health concern.
Symptoms of Rheumatic Fever

Rheumatic fever can present with a variety of symptoms, which may vary in severity. The primary symptoms include fever, joint pain and inflammation, particularly in the knees, ankles, elbows, and wrists. Other common symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, and a rash known as erythema marginatum. In some cases, individuals may experience secondary symptoms such as heart murmurs or abnormal heart rhythms. It is important to note that these symptoms may not immediately follow a streptococcal infection but can develop weeks later.
Primary symptoms of Rheumatic Fever

Primary symptoms of Rheumatic Fever usually develop within a few weeks after a streptococcal infection, such as strep throat or scarlet fever. The most common symptom is a fever, which is often accompanied by joint pain and swelling, especially in the knees, ankles, elbows, and wrists. In addition to joint symptoms, individuals with Rheumatic Fever may experience chest pain and shortness of breath due to inflammation of the heart. Other primary symptoms include fatigue, rash, nodules under the skin, and uncontrollable movements of the arms and legs known as Sydenham's chorea. These symptoms can vary in severity from mild to severe and may come and go over time. If any of these primary symptoms are present, it is crucial to seek medical attention for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
Secondary symptoms of Rheumatic Fever

Secondary symptoms of Rheumatic Fever are typically related to the inflammation and damage caused by the disease. These symptoms may manifest in different parts of the body, including joints, heart, skin, and nervous system. Joint symptoms often include pain, swelling, and stiffness in multiple joints, resembling rheumatoid arthritis. Cardiac symptoms may include chest pain or discomfort, palpitations, or shortness of breath. Skin symptoms can present as red rashes or nodules on the skin. Neurological symptoms may include abnormal movements or involuntary jerking of the limbs. It is important to recognize these secondary symptoms and seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Causes of Rheumatic Fever

Rheumatic Fever is primarily caused by a bacterial infection called Group A Streptococcus. When left untreated or inadequately treated, the bacteria can trigger an immune response in the body, leading to the development of Rheumatic Fever. However, not everyone who experiences a strep infection will develop Rheumatic Fever. Other factors such as genetic predisposition and environmental influences also play a role in determining the likelihood of developing the condition. It is important to promptly treat any strep throat infections to minimize the risk of Rheumatic Fever.
Bacterial infection and Rheumatic Fever

Bacterial infection plays a crucial role in the development of Rheumatic Fever. Specifically, it is caused by an infection with the bacteria Streptococcus pyogenes, which is responsible for strep throat. When left untreated, this bacteria can trigger an abnormal immune response in individuals, leading to the onset of Rheumatic Fever. The bacteria's antigens resemble certain proteins found in our own body tissues, such as those in the heart or joints. As a result, the immune system mistakenly attacks these tissue proteins, causing inflammation and damage to these organs. Understanding the connection between bacterial infection and Rheumatic Fever is vital for effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Genetic and environmental factors of Rheumatic Fever

Genetic and environmental factors play a significant role in the development of Rheumatic Fever. Some individuals may have a genetic susceptibility to the disease, making them more prone to developing it after an infection. Certain variations in genes that regulate the body's immune response can increase the risk.
Environmental factors also contribute to the development of Rheumatic Fever. Crowded living conditions, poor sanitation, and limited access to healthcare increase the prevalence of streptococcal infections, which can lead to Rheumatic Fever. Additionally, exposure to streptococcal bacteria in school or daycare settings can increase the risk of infection. Identifying these genetic and environmental factors are important for preventing and managing the disease effectively.
Risk Factors of Rheumatic Fever

Certain factors can increase the risk of developing Rheumatic Fever. Age, gender, and ethnicity play a role, as children aged 5 to 15 and individuals of Maori or Pacific Islander descent are more susceptible. Additionally, medical conditions such as strep throat or scarlet fever can increase the risk. Poor living conditions and overcrowding can also contribute to the spread of bacterial infections that lead to Rheumatic Fever. Unhealthy lifestyle habits like smoking and a lack of proper hygiene further heighten the risk. Awareness and addressing these factors are crucial in preventing Rheumatic Fever.
Age, gender, and ethnicity and their risk factors of Rheumatic Fever

Certain factors such as age, gender, and ethnicity can influence the risk of developing Rheumatic Fever. Children between the ages of 5 and 15 are most commonly affected, although it can occur at any age.
Medical conditions and lifestyle habits that increase the risk of Rheumatic Fever

Certain medical conditions and lifestyle habits can increase the risk of developing Rheumatic Fever. People with a history of strep throat or scarlet fever are more susceptible to developing the condition. Additionally, individuals with a weakened immune system due to pre-existing conditions such as HIV/AIDS or malnutrition may have a higher risk. Poor living conditions, overcrowding, and lack of access to healthcare also contribute to the increased prevalence of Rheumatic Fever in certain populations. Furthermore, individuals who do not receive prompt and adequate treatment for strep throat are at a greater risk of developing Rheumatic Fever.
Diagnostic Procedures for Rheumatic Fever

To diagnose Rheumatic Fever, doctors typically begin by conducting a physical examination and reviewing the patient's medical history. During the physical examination, the doctor pays close attention to symptoms such as joint pain, fever, and inflammation. Blood tests may be performed to check for certain antibodies and markers of inflammation in the blood. An electrocardiogram (ECG) may also be done to assess the heart's electrical activity and detect any abnormalities. These diagnostic procedures help healthcare professionals determine if a person has Rheumatic Fever and guide them in developing an appropriate treatment plan.
Physical examination and medical history
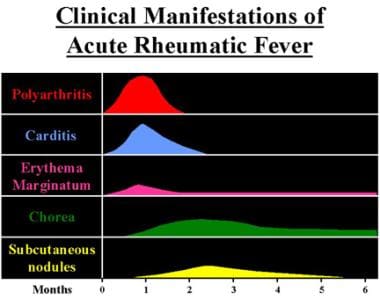
During a physical examination, a healthcare provider will assess the patient's overall health and look for specific signs and symptoms of Rheumatic Fever. They may check the joints for swelling, tenderness, and limited range of motion. Additionally, they will listen to the heart for any abnormalities, such as a heart murmur. The medical history is also crucial in diagnosing Rheumatic Fever. The healthcare provider will inquire about recent strep throat infections, previous episodes of Rheumatic Fever, and any family history of the disease. This information helps in determining the likelihood of Rheumatic Fever and guiding further diagnostic tests and treatment options.
Blood tests and electrocardiogram for Rheumatic Fever diagnosis
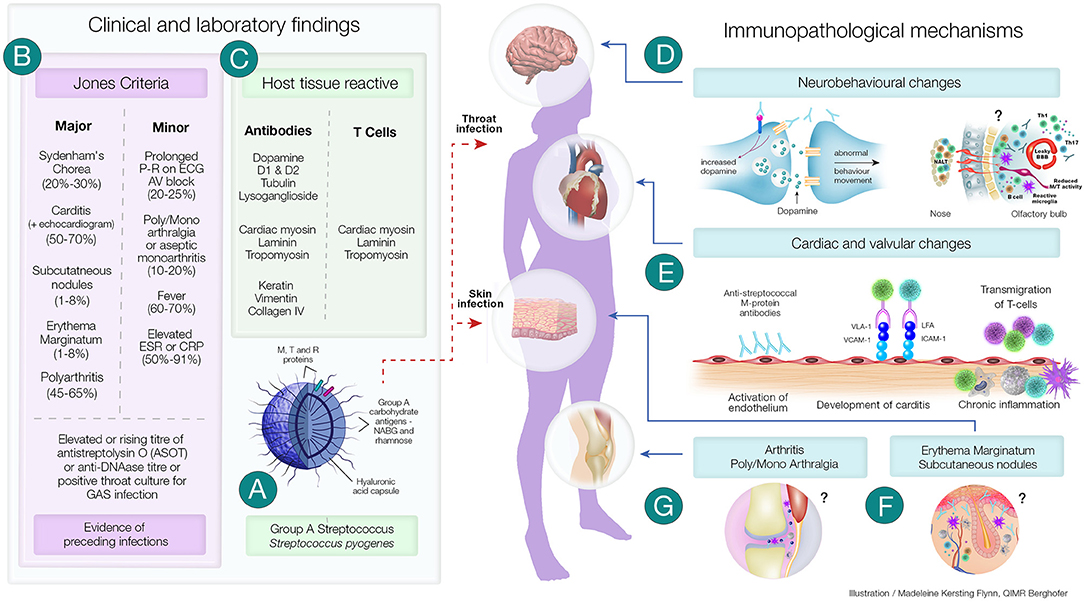
Blood tests and an electrocardiogram (ECG) are commonly used diagnostic procedures to confirm a diagnosis of Rheumatic Fever. Blood tests help to detect the presence of certain antibodies in the blood that are indicative of an active streptococcal infection. Additionally, blood tests can also measure the levels of inflammation markers in the body. An ECG, on the other hand, measures the electrical activity of the heart and can reveal any abnormal heart rhythms or damage to the heart valves caused by Rheumatic Fever. These diagnostic procedures are crucial in promptly identifying and treating Rheumatic Fever to prevent complications.
Treatment for Rheumatic Fever

Treatment for Rheumatic Fever focuses on managing symptoms, reducing inflammation, and preventing further complications. The primary approach involves the use of antibiotics to treat the underlying bacterial infection. These medications help eliminate the bacteria causing the infection and prevent it from spreading. Additionally, anti-inflammatory drugs such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are often prescribed to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. In severe cases, where there is damage to the heart valves, surgery may be necessary to repair or replace the affected valves. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers are essential to monitor progress and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
Antibiotics and anti-inflammatories for Rheumatic Fever treatment

Antibiotics and anti-inflammatories are commonly used in the treatment of Rheumatic Fever. Antibiotics are prescribed to eliminate the bacteria responsible for causing the initial infection, such as streptococcus bacteria. This helps to prevent the recurrence of Rheumatic Fever and reduce the risk of complications. Anti-inflammatory medication, on the other hand, is used to reduce inflammation in the affected joints, heart, and other organs. These medications help alleviate pain and discomfort associated with Rheumatic Fever, allowing patients to resume their normal activities. It is important for patients to take their prescribed medications as directed by their healthcare provider in order to effectively manage their Rheumatic Fever symptoms.
Surgery and hospitalization options for severe Rheumatic Fever cases

In severe cases of Rheumatic Fever, surgery and hospitalization may be necessary to manage the complications and provide effective treatment. Hospitalization allows for close monitoring of the patient's condition, ensuring prompt intervention in case of any deterioration. Surgical interventions may be required to repair or replace damaged heart valves or correct any other cardiovascular abnormalities resulting from the disease. These procedures aim to restore the normal function of the heart and improve the patient's overall health. The decision to undergo surgery or hospitalization is made by medical professionals based on individual assessment and the severity of the Rheumatic Fever.
Complications of Rheumatic Fever

Complications of Rheumatic Fever can be serious and can affect various parts of the body. One of the most common complications is damage to the heart valves, known as Rheumatic Heart Disease. This occurs when the heart valves become scarred and stiff, leading to problems with blood flow. Other complications may include inflammation of the lining around the heart (pericarditis), inflammation of the brain (encephalitis), joint deformities, and skin nodules. In rare cases, Rheumatic Fever can also lead to heart failure or life-threatening infections. Proper treatment and follow-up care are essential to prevent these complications and ensure long-term health.
Potential complications of Rheumatic Fever
Potential complications of Rheumatic Fever can vary in severity and affect different parts of the body. The most common complication is damage to the heart valves, known as rheumatic heart disease. This occurs when the immune response triggered by the bacterial infection affects the valves, causing them to become scarred and stiff. Other potential complications include inflammation of the lining surrounding the heart (pericarditis), heart failure, and abnormal heart rhythms. In some cases, Rheumatic Fever can also lead to joint deformities or neurological problems such as Sydenham's chorea, a movement disorder. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in order to prevent these complications from occurring or worsening.
Long-term effects and prognosis for Rheumatic Fever

Long-term effects of Rheumatic Fever can vary depending on the severity of the initial infection and the effectiveness of treatment. In some cases, damage to the heart valves may occur, leading to a condition known as rheumatic heart disease. This can result in symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and chest pain. Additionally, individuals who have had Rheumatic Fever are at a higher risk for future episodes of the disease if they are exposed to streptococcal infections again. Prognosis also depends on appropriate and timely treatment. Regular medical follow-up and adherence to preventive measures can help manage symptoms and improve long-term outcomes for those with Rheumatic Fever.
Prevention of Rheumatic Fever

Prevention of Rheumatic Fever plays a crucial role in minimizing the risk of developing this condition. Maintaining good hygiene practices, such as washing hands frequently and avoiding close contact with individuals who have strep throat or other infections, is essential. Vaccinations can also help protect against certain bacterial infections that can lead to Rheumatic Fever. Individuals with a history of Rheumatic Fever should receive regular medical check-ups and adhere to antibiotic prophylaxis, which involves taking antibiotics before certain medical procedures or dental visits. By implementing these preventative measures, the likelihood of developing Rheumatic Fever can be significantly reduced.
Hygiene and infection prevention methods

Hygiene and infection prevention methods play a crucial role in reducing the risk of rheumatic fever. Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly, can help minimize the spread of bacteria that can lead to infections. It is also important to maintain a clean and healthy environment by keeping surfaces sanitized and promoting proper ventilation. Additionally, avoiding close contact with individuals who have respiratory infections or strep throat can help prevent the transmission of bacteria that may trigger rheumatic fever. By implementing these simple yet effective measures, individuals can significantly reduce their chances of developing this condition.
Vaccinations and other preventative measures for Rheumatic Fever

In order to prevent Rheumatic Fever, vaccinations are an important preventative measure. The most common vaccine used is the Group A Streptococcus vaccine, which helps protect against the bacterial infection that can lead to Rheumatic Fever. Regular vaccinations are recommended for individuals at high risk, such as those with a previous history of the disease or those living in overcrowded conditions. Additionally, maintaining good personal hygiene, practicing proper handwashing techniques, and avoiding close contact with infected individuals can also help prevent the spread of the bacteria that causes Rheumatic Fever.
Conclusion

In conclusion, Rheumatic Fever is a serious condition that primarily affects the joints, heart, and other organs. The disease is caused by an untreated or inadequately treated streptococcal infection. It is characterized by symptoms such as joint pain, fever, and inflammation. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications and long-term damage. Treatment options include antibiotics to eliminate the bacteria and anti-inflammatory medications to alleviate symptoms. It is crucial to practice good hygiene and receive necessary vaccinations to prevent the onset of Rheumatic Fever.
Summary of Rheumatic Fever symptoms, causes, and treatment options

Rheumatic Fever is a serious condition that can affect various parts of the body, including the heart, joints, and brain. Common symptoms include fever, joint pain and swelling, chest pain, and shortness of breath. It is primarily caused by a bacterial infection called Streptococcus pyogenes, although genetic and environmental factors also play a role. Treatment involves the use of antibiotics to eliminate the infection and anti-inflammatory medications to reduce inflammation. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary. Preventative measures include good hygiene practices and vaccinations against certain diseases that can trigger Rheumatic Fever.
Additional resources and community support for individuals with Rheumatic Fever.
Individuals diagnosed with Rheumatic Fever can benefit from various additional resources and community support systems. In many countries, there are organizations dedicated to raising awareness about this condition and providing resources for those affected. These organizations may offer educational materials, support groups, online forums, and helplines for individuals seeking information or emotional support. Additionally, healthcare professionals and specialized centers can provide guidance and counseling on managing the symptoms and long-term effects of Rheumatic Fever. Connecting with these resources can empower individuals to better understand their condition and find the support they need.

