Introduction to Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)

Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints. It is characterized by inflammation and pain in the joints, particularly in the hands, feet, and wrists. RA can also affect other parts of the body, such as the eyes, lungs, and heart.
Unlike osteoarthritis, which is caused by wear and tear on the joints, rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition. This means that the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues, including the synovium - a thin membrane that lines the joints. Over time, this inflammation can lead to damage in the cartilage and bones of the joints.
The symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis can vary greatly from person to person. Some may experience mild joint pain and stiffness, while others may have severe swelling and deformity in their joints. Fatigue, fever, and weight loss are also common symptoms.
While there is currently no cure for rheumatoid arthritis, there are various treatment options available to manage the symptoms and slow down the progression of the disease. These may include medications to reduce inflammation and pain, physical therapy to improve joint function and mobility, as well as lifestyle changes such as regular exercise and a healthy diet.
It is important for individuals with rheumatoid arthritis to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs. With proper management and care, it is possible for individuals with RA to lead fulfilling lives.
What causes Rheumatoid Arthritis?
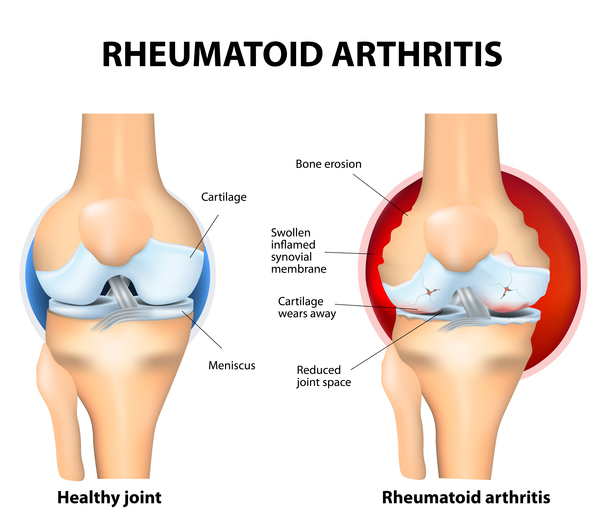
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints. While the exact cause of RA is still unknown, researchers believe that it is a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
The immune system plays a crucial role in the development of Rheumatoid Arthritis. In individuals with RA, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy joint tissues, causing inflammation, pain, and swelling. This misguided immune response leads to the destruction of cartilage and bone around the joints.
Furthermore, scientists have identified certain risk factors that may contribute to the development of Rheumatoid Arthritis. These include smoking, obesity, hormonal changes in women, and exposure to certain infections. However, it's important to note that these factors alone are not sufficient to cause RA. They simply increase the likelihood of developing the condition in individuals who are genetically predisposed.
Osteoclasts, a type of bone cell involved in bone remodeling, also play a significant role in Rheumatoid Arthritis development. Research suggests that osteoclasts become overly active in individuals with RA, leading to the erosion of bone tissue around affected joints.
While we have yet to identify a definitive cause for Rheumatoid Arthritis, ongoing research is uncovering more about its complex nature. Understanding these factors can help advance treatments and management strategies for those living with this debilitating condition.
The role of genetics in Rheumatoid Arthritis
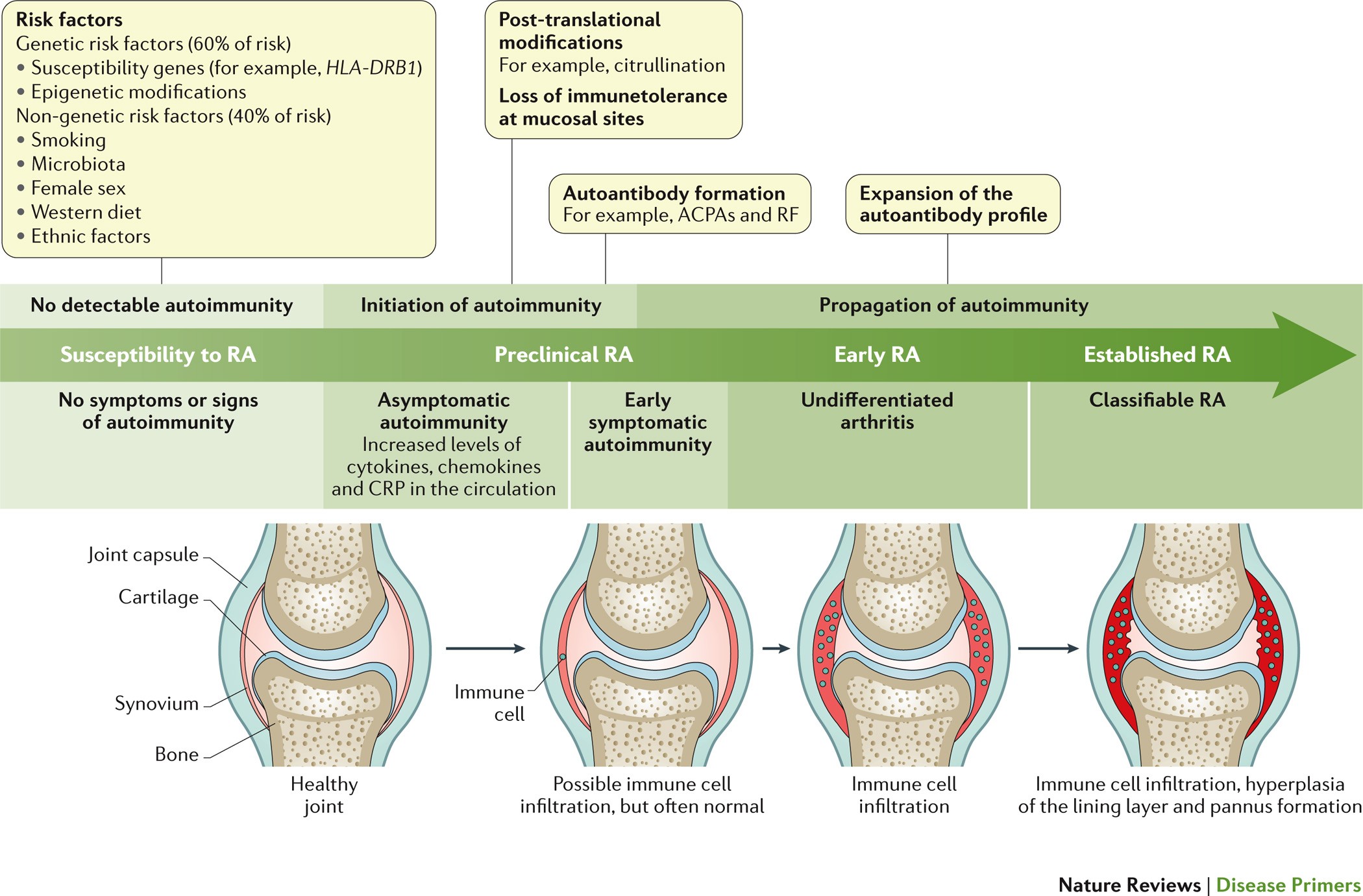
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a complex disease that involves the immune system mistakenly attacking the body's own tissues, particularly the joints. While the exact cause of RA is still not fully understood, research has shown a strong genetic component in its development.
Genetics plays a significant role in determining an individual's susceptibility to developing RA. Studies have found that individuals with a family history of RA are more likely to develop the condition themselves. In fact, having a first-degree relative, such as a parent or sibling, with RA can increase a person's risk by two to three times compared to those without a family history.
The genes associated with RA are believed to influence the immune system's response and regulation, as well as joint inflammation and destruction. Specifically, variations in certain genes involved in immune function and inflammation, such as HLA-DRB1 and PTPN22, have been identified as potential contributors to the development of RA.
It is important to note that while genetics play a significant role in determining the risk of developing RA, it does not guarantee that someone will develop the condition. Other factors such as environmental triggers and lifestyle choices also play a role in the onset and progression of RA.
Understanding the role of genetics in Rheumatoid Arthritis is crucial for early detection and better management of the condition. Genetic testing can help identify individuals at higher risk, allowing for proactive measures such as lifestyle modifications or monitoring for early signs and symptoms.
How is Rheumatoid Arthritis inherited?
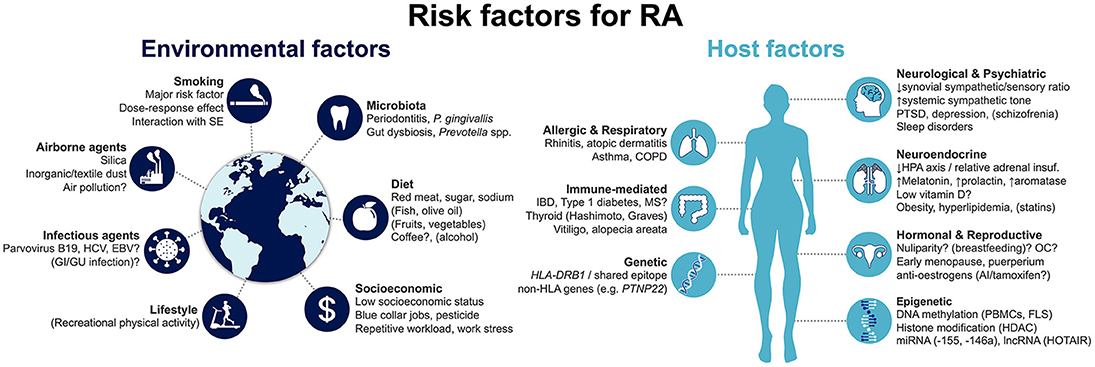
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is believed to have a genetic component, which means that the risk of developing the condition can be inherited from family members. However, it is important to note that having a family history of RA does not guarantee that an individual will develop the disease.
The inheritance pattern of RA is complex and not fully understood. Multiple genes are thought to interact with each other and with environmental factors to increase the risk of developing the condition. In fact, research suggests that more than 100 genes may be involved in the development of RA.
Studies have shown that individuals who have a first-degree relative, such as a parent or sibling, with RA are at a slightly higher risk of developing the disease compared to those without a family history. The risk increases if both parents have RA.
It is also worth mentioning that having certain gene variations, such as HLA-DRB1 alleles, has been strongly associated with an increased risk of developing RA. These genes are involved in the immune system's response and may play a role in triggering autoimmune reactions seen in RA.
While genetics can contribute to the risk of developing Rheumatoid Arthritis, it is important to remember that other factors, such as environmental triggers and lifestyle choices, also play a significant role in the development and progression of the disease.
Genes linked to Rheumatoid Arthritis

Genes play a significant role in the development of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). Several specific genes have been identified that are linked to an increased risk of developing this autoimmune disease. One of the most well-known genetic factors associated with RA is the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) gene complex. Variants of this gene, particularly HLA-DRB1 alleles, have been found to be strongly associated with an increased susceptibility to RA.
In addition to the HLA gene complex, other genes have also been implicated in the development of RA. For example, certain variants of the PTPN22 gene and the STAT4 gene have been identified as risk factors for the disease. These genes are involved in regulating immune responses and inflammation, both of which are key factors in the pathogenesis of RA.
It is important to note that while these genetic factors increase the risk of developing RA, they do not guarantee that an individual will develop the disease. The presence or absence of these genes merely influences susceptibility to RA. Environmental factors and lifestyle choices also play a significant role in triggering RA in susceptible individuals.
Understanding these genetic links to RA can help researchers better understand the underlying mechanisms of the disease and potentially develop targeted therapies. However, more research is needed to fully understand how these genetic factors interact with environmental triggers to cause Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Other factors that contribute to Rheumatoid Arthritis
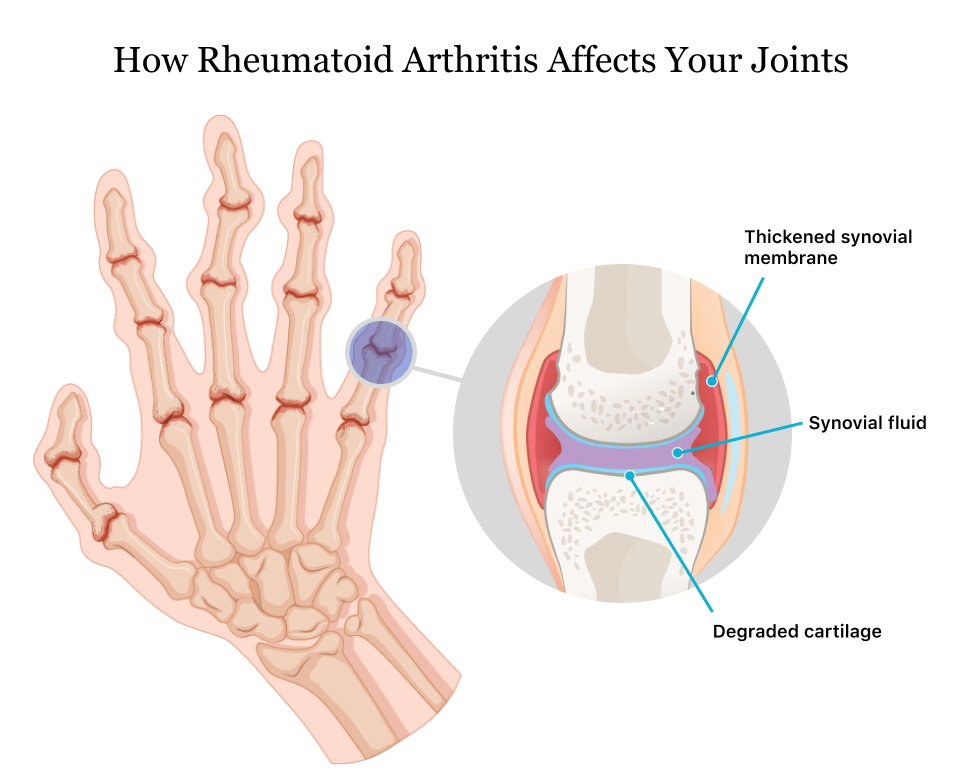
In addition to genetics, there are several other factors that contribute to the development of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). Environmental factors play a significant role in triggering the onset of RA in individuals with a genetic predisposition. Exposure to certain environmental factors such as smoking, air pollution, and infections can increase the risk of developing the disease.
Smoking has been identified as a major risk factor for RA. Studies have shown that smokers are at a higher risk of developing RA compared to non-smokers. It is believed that smoking activates certain genes that are involved in the development of RA and also affects the immune system, leading to chronic inflammation.
Furthermore, exposure to air pollution has also been linked to an increased risk of RA. Pollutants found in air pollution can trigger an inflammatory response and contribute to the development and progression of RA.
Infections, particularly periodontal infections caused by bacteria, have also been associated with an increased risk of developing RA. The presence of certain bacteria in the mouth can lead to chronic inflammation and affect the immune system, potentially contributing to the development of RA.
It is important to note that while these factors may increase the risk of developing RA, not everyone exposed to them will develop the disease. The interplay between genetics and environmental factors is complex and further research is needed to fully understand their role in Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Can Rheumatoid Arthritis be prevented or predicted?

Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and stiffness. While there is currently no known cure for RA, researchers have been studying ways to prevent or predict its development.
Preventing Rheumatoid Arthritis entirely is not yet possible. However, there are certain lifestyle changes that individuals can adopt to reduce their risk of developing the condition. Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and avoiding smoking have all been associated with a lower risk of RA. Additionally, a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids may help promote joint health.
In terms of prediction, scientists have made strides in identifying certain factors that can increase the likelihood of developing Rheumatoid Arthritis. Genetic testing can identify specific genes associated with an increased risk of RA. This information can be valuable for individuals who have a family history of the disease.
While prevention and prediction are important areas of research, early diagnosis remains crucial for optimal outcomes in managing RA. Recognizing the early signs and symptoms such as joint pain and swelling allows for timely intervention and treatment. This can help slow down disease progression and minimize potential joint damage.
In conclusion, while Rheumatoid Arthritis cannot currently be prevented entirely, individuals can lower their risk through lifestyle modifications. Additionally, advances in genetic testing offer insights into the inherited risk of RA. Early diagnosis remains paramount in effectively managing the condition and improving quality of life for those affected by this complex autoimmune disease.
Early diagnosis and treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Early diagnosis and treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis are crucial for managing the condition effectively and preventing long-term joint damage. Detecting Rheumatoid Arthritis in its early stages allows healthcare professionals to intervene and implement appropriate treatment plans promptly.
Diagnosing Rheumatoid Arthritis typically involves a combination of patient history, physical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. The sooner the condition is diagnosed, the sooner treatment can begin. Early treatment aims to control inflammation and prevent further joint damage.
A variety of medications are available to manage Rheumatoid Arthritis. These include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biologic agents. The specific medications used depend on factors such as the severity of symptoms and the patient's overall health.
Aside from medication, physical therapy can play a significant role in managing Rheumatoid Arthritis. Physical therapists can help patients learn exercises that improve joint flexibility, strengthen surrounding muscles, and reduce pain.
It's important for patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis to collaborate closely with their healthcare team to fine-tune their treatment plan based on individual needs. Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor progress, adjust medications if necessary, and address any concerns or complications that may arise.
In conclusion, early diagnosis and prompt treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis are crucial for successful management of the condition. Effective communication with healthcare professionals and adherence to recommended treatment plans can significantly improve quality of life for individuals living with this chronic autoimmune disease.
Conclusion and key takeaways for understanding inherited risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis

In conclusion, it is clear that there is a genetic component to the development of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). While the exact causes of RA are still being studied, research has shown that genetics play a significant role in determining an individual's risk for developing the condition. Individuals with a family history of RA have a higher likelihood of developing the disease themselves.
Understanding the inherited risk of RA can help individuals make informed decisions about their health and take preventative measures if necessary. It is important for those with a family history of RA to be proactive in monitoring their health and seeking early medical intervention if they experience symptoms such as joint pain, swelling, or stiffness.
However, it is also important to note that genetics are not the sole determinant of RA. Other factors such as environmental triggers and lifestyle choices can also contribute to the development of the disease. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, a balanced diet, and minimizing exposure to known triggers can help reduce the risk of developing RA or manage symptoms if already diagnosed.
In summary, while Rheumatoid Arthritis may have a genetic component, it is not entirely determined by genetics alone. By understanding one's inherited risk and making proactive choices regarding lifestyle and health care, individuals can better manage their risks and potentially delay or prevent the onset of Rheumatoid Arthritis.

