It is crucial to understand the silent threat that osteoporosis poses to our bone health. Osteoporosis is a condition that weakens bones, making them fragile and more prone to fractures. The alarming fact is that it often goes unnoticed until a fracture occurs.
What is Osteoporosis and why is it a silent threat?
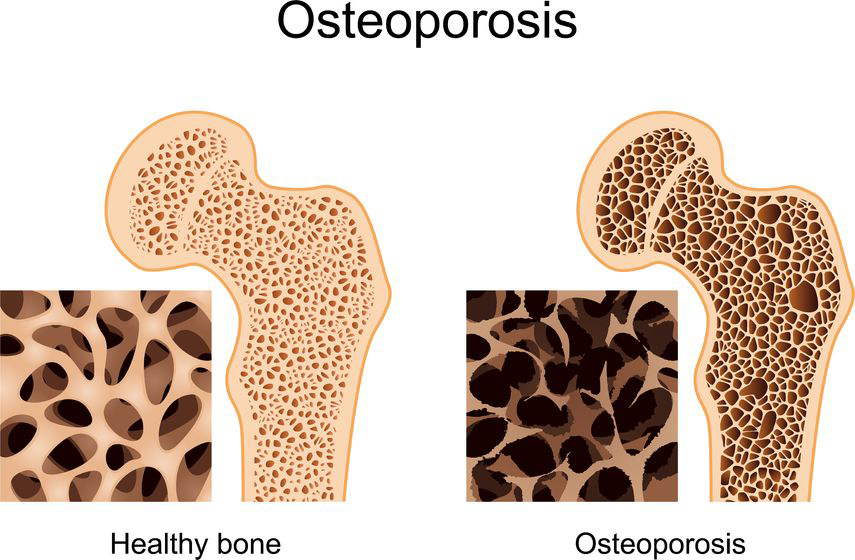
Osteoporosis is a degenerative bone disease characterized by a decrease in bone density and quality. The silent threat lies in the fact that it progresses without any symptoms or warning signs until a fracture occurs. Many people are unaware that they have osteoporosis until they experience a bone fracture, which can be incredibly debilitating and life-changing.
Causes and risk factors of Osteoporosis
Several factors can increase the risk of developing osteoporosis. Age is a significant risk factor, as bone density naturally decreases as we get older. Women, especially after menopause, are more susceptible to osteoporosis due to hormonal changes. Lack of calcium and vitamin D in the diet, sedentary lifestyle, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and certain medical conditions or medications can also contribute to the development of osteoporosis.
By understanding the silent threat that osteoporosis poses, we can take proactive steps to protect our bone health. Regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, and avoiding harmful lifestyle habits can help reduce the risk. It is also important to undergo regular bone density tests as we age, especially if we have risk factors or a family history of osteoporosis.
Remember, prevention and early detection are key in combating osteoporosis and maintaining strong and healthy bones.
Understanding Bone and Joint Inflammation: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
Hip replacement: A surgical procedure that involves replacing a damaged hip joint with an artificial one
Promising Research and Developments for Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatments
Rheumatoid Arthritis in Children: Signs, Symptoms, and Treatment
Overcoming Fatigue and Depression Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis
The Relationship Between Diet and Rheumatoid Arthritis Management
When to Seek Medical Help for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Key Differences Between Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis
Living with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Coping Strategies and Treatment Options
Understanding the Symptoms and Causes of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a silent threat to bone health as it often goes unnoticed until a fracture occurs. To take proactive steps in protecting bone health, it is important to be aware of the common symptoms of osteoporosis and the diagnostic tests available for early detection.
Common symptoms of Osteoporosis
While osteoporosis itself may not cause any noticeable symptoms, certain signs can indicate its presence. These include gradual loss of height, stooped posture, back pain, and fractures that occur even from minor incidents. It is important to pay attention to these signs, especially in older adults, as they can indicate bone density loss.
Diagnostic tests for Osteoporosis
To diagnose osteoporosis, doctors may recommend a bone mineral density (BMD) test. One common technique for measuring BMD is dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA). This test evaluates bone density at various sites, such as the hip, spine, and wrist. The results are compared to a healthy young adult of the same sex to determine bone density status.
Another diagnostic method is a quantitative ultrasound (QUS) test, which measures sound wave transmission through the bone to assess its density and strength. This test is often used for screening purposes and can provide valuable information about bone health.
Early diagnosis through these tests is crucial, as it allows for timely intervention to prevent further bone loss and fractures. If osteoporosis is detected, treatment options like medication, calcium and vitamin D supplements, and lifestyle modifications can be recommended to manage the condition effectively.
By understanding the symptoms and diagnostic tests for osteoporosis, individuals can take the necessary steps towards early detection and treatment, ensuring better long-term bone health. Regular screenings and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help mitigate the impact of this silent threat and promote stronger bones for a better quality of life

Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
Osteoporosis is a silent threat to bone health that often goes unnoticed until a fracture occurs. To protect bone health and prevent the development of osteoporosis, certain lifestyle changes and preventive measures can be taken. Here, we will explore the role of nutrition in maintaining bone health and the importance of exercise and physical activity for strong bones.
The role of nutrition in maintaining bone health
Proper nutrition plays a crucial role in maintaining strong and healthy bones. Calcium, vitamin D, and other essential nutrients are vital for bone health. Consuming a balanced diet that includes calcium-rich foods such as dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and fortified foods can help ensure adequate calcium intake. Additionally, getting enough vitamin D from sunlight exposure or through dietary sources like fatty fish and fortified foods is essential for calcium absorption. Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption and limiting the intake of caffeine and sodium can also contribute to maintaining optimal bone health.
Exercise and physical activity for strong bones
Regular exercise and physical activity are key factors in building and maintaining strong bones. Weight-bearing exercises such as walking, jogging, dancing, and weightlifting help stimulate bone growth and increase bone density. Strength training exercises that target the major muscle groups also play a crucial role in improving bone health. Engaging in at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise and strength training activities on most days of the week can significantly contribute to maintaining healthy bones.
By incorporating these preventive measures and lifestyle changes, individuals can take proactive steps toward preventing osteoporosis and maintaining optimal bone health. It is essential to consult with healthcare professionals and undergo regular screenings to assess bone density and receive appropriate guidance on preventive and treatment strategies. With a focus on nutrition, exercise, and overall healthy lifestyle choices, the impact of this silent threat can be mitigated, ensuring better long-term bone health and a higher quality of life.

Treatment Options for Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis, a silent threat to bone health, can have devastating consequences if left untreated. Luckily, there are several treatment options available to manage and prevent further bone loss. In this article, we will explore the various medications used to treat osteoporosis, as well as other treatment options and therapies that can help improve bone health.
Medications for Osteoporosis
There are several medications that can be prescribed to slow down bone loss, increase bone density, and reduce the risk of fractures in individuals with osteoporosis. These medications fall into two main categories: antiresorptive drugs and anabolic drugs.
Antiresorptive drugs, such as bisphosphonates, work by slowing down the activity of the cells that break down bone. They help to maintain bone mass and reduce the risk of fractures. Other antiresorptive drugs include selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), hormone replacement therapy (HRT), and calcitonin.
Anabolic drugs, such as teriparatide and abaloparatide, work by stimulating new bone growth. These medications are usually recommended for individuals with severe osteoporosis or those who have experienced multiple fractures.
Other Treatment Options and Therapies
In addition to medication, there are other treatment options and therapies that can help improve bone health and reduce the risk of fractures. These include:
Calcium and Vitamin D Supplements: Adequate calcium and vitamin D intake is essential for maintaining strong bones. Supplements may be recommended for individuals who do not get enough of these nutrients from their diet.
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help improve balance, strength, and flexibility, reducing the risk of falls and fractures.
Lifestyle Changes: Engaging in weight-bearing exercises, such as walking or dancing, can help strengthen bones. Quitting smoking and reducing alcohol consumption can also improve bone health.
Fall Prevention: Making modifications to the home environment, using assistive devices, and practicing good balance and posture can help prevent falls and fractures.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment options for your specific condition. Regular screenings and check-ups are also crucial to monitor bone density and assess the effectiveness of the chosen treatment plan. By taking proactive steps to manage osteoporosis, individuals can protect their bone health and maintain a higher quality of life.

Living with Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a silent threat to bone health and can have devastating consequences if left untreated. It is important for individuals with osteoporosis to learn how to manage their daily activities and access the support and resources available to them.
Managing daily activities with Osteoporosis
Living with osteoporosis requires individuals to make certain adjustments to their daily activities to protect their bones and prevent fractures. Here are some tips for managing daily activities with osteoporosis:
Exercise: Engaging in weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, dancing, or gardening, can help strengthen bones and improve overall bone health. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine suitable exercises based on individual needs and capabilities.
Proper body mechanics: Individuals with osteoporosis should learn proper body mechanics to avoid activities that put excessive stress on the bones, such as lifting heavy objects or bending at the waist. It is important to use the legs to lift objects and to avoid twisting or sudden movements that can increase the risk of fractures.
Home modifications: Making modifications to the home environment can help reduce the risk of falls and fractures. This can include installing handrails in bathrooms and staircases, removing tripping hazards, ensuring proper lighting, and using non-slip mats.
Support and resources for individuals with Osteoporosis
Living with osteoporosis can be challenging, but there are many support and resources available to individuals to help them manage their condition. Here are some of the resources that individuals with osteoporosis can access for support:
Support groups: Joining support groups can provide individuals with osteoporosis an opportunity to connect with others who are facing similar challenges, share experiences, and receive emotional support.
Healthcare professionals: Consulting with healthcare professionals, such as doctors, nurses, and physical therapists, can provide individuals with valuable guidance on managing osteoporosis, including medication management, lifestyle modifications, and exercises.
Education and information: Accessing information and educational resources about osteoporosis can help individuals better understand their condition and make informed decisions about their healthcare. This can include websites, brochures, and educational materials provided by reputable organizations and healthcare institutions.
By managing daily activities and accessing the support and resources available, individuals with osteoporosis can improve their quality of life and minimize the impact of the condition on their bone health. It is important to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized management plan that suits individual needs and conditions.

