Introduction to Osteoarthritis Research and Treatment
Overview of Osteoarthritis and its impact
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that affects millions of people worldwide. This condition is characterized by the breakdown of cartilage in the joints, causing pain, stiffness, and loss of mobility. It can affect any joint in the body, but it is most common in weight-bearing joints such as the hips, knees, and spine.
Osteoarthritis can have a significant impact on an individual's quality of life, limiting their ability to perform daily tasks and participate in activities they enjoy. As it progresses, it may require joint replacement surgery, which can be costly and have a long recovery time.
Current state of Osteoarthritis research and treatment
While there is currently no cure for osteoarthritis, research has made significant strides in understanding the disease and developing treatments to manage symptoms. This includes medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and corticosteroids, as well as physical therapy and exercise programs.
In recent years, there has been a focus on developing new treatments that can slow or even reverse the progression of the disease. This includes the use of stem cells and other regenerative medicine techniques to repair damaged cartilage and improve joint function.
Additionally, there has been an increased emphasis on personalized medicine approaches to osteoarthritis treatment, taking into account an individual's unique genetic and lifestyle factors that may impact their disease progression.
Overall, while there is still much to learn about osteoarthritis, advancements in research and treatment options offer hope for those affected by this debilitating condition.

Understanding Osteoarthritis
Causes and Symptoms of Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease that affects millions of people globally, occurs due to the gradual breakdown of cartilage in the joints. The most common cause of this condition is ageing, but other factors such as genetics, obesity, and joint injuries also contribute to its development.
The symptoms of osteoarthritis include joint pain and inflammation, stiffness, and loss of mobility. The severity of these symptoms varies between individuals, and they tend to get worse over time.
Stages of Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis progresses in stages starting from mild pain and discomfort to severe pain and loss of mobility. In the early stages, individuals may experience joint pain only during strenuous activities, which may subside with rest. During the moderate stage, the pain becomes frequent and may interfere with daily activities. In severe cases, the pain becomes constant, and joint deformity may occur.
While there is currently no cure for osteoarthritis, research has led to significant developments in treatment options that help manage symptoms. These include the use of medication such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and corticosteroids to control pain and inflammation, physical therapy and exercise programs to strengthen muscles and improve joint function.
Recent advancements in research have focused on developing new treatments that aim to slow or even reverse the progression of the disease. Such treatments include the use of stem cells and other regenerative techniques to repair damaged cartilage and improve joint function.
Overall, while osteoarthritis can have a significant impact on an individual's quality of life, the advancements in research and treatment options offer hope for those affected by the condition.

Osteoarthritis is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is caused by the gradual breakdown of cartilage in the joints, and while ageing is the most common cause, other factors such as genetics, obesity, and joint injuries also contribute to its development. The symptoms of osteoarthritis include joint pain and inflammation, stiffness, and loss of mobility, which tend to worsen over time.
While there is no cure for osteoarthritis, various treatment options are available to manage its symptoms. Traditional treatment methods include medication, physical therapy, and exercise programs. Medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and corticosteroids are used to control pain and inflammation. These drugs are effective in reducing pain, but they come with potential side effects, especially if used for extended periods.
Physical therapy and exercise programs are another treatment option for osteoarthritis. These programs are designed to strengthen muscles, improve joint function, and relieve pain. Physical therapy may include manual therapy, such as massage and joint mobilization. Exercise programs may include low-impact activities such as swimming and cycling, which can help maintain joint flexibility and improve overall fitness.
Overall, traditional treatment methods can help manage the symptoms of osteoarthritis, but they cannot cure the condition. New advancements in research are focusing on developing new treatments that aim to slow or even reverse the progression of the disease. These include the use of stem cells and other regenerative techniques to repair damaged cartilage and improve joint function.
In conclusion, osteoarthritis can have a significant impact on an individual's quality of life, but with early diagnosis and effective treatment, it is possible to manage its symptoms and maintain joint function for an extended period.
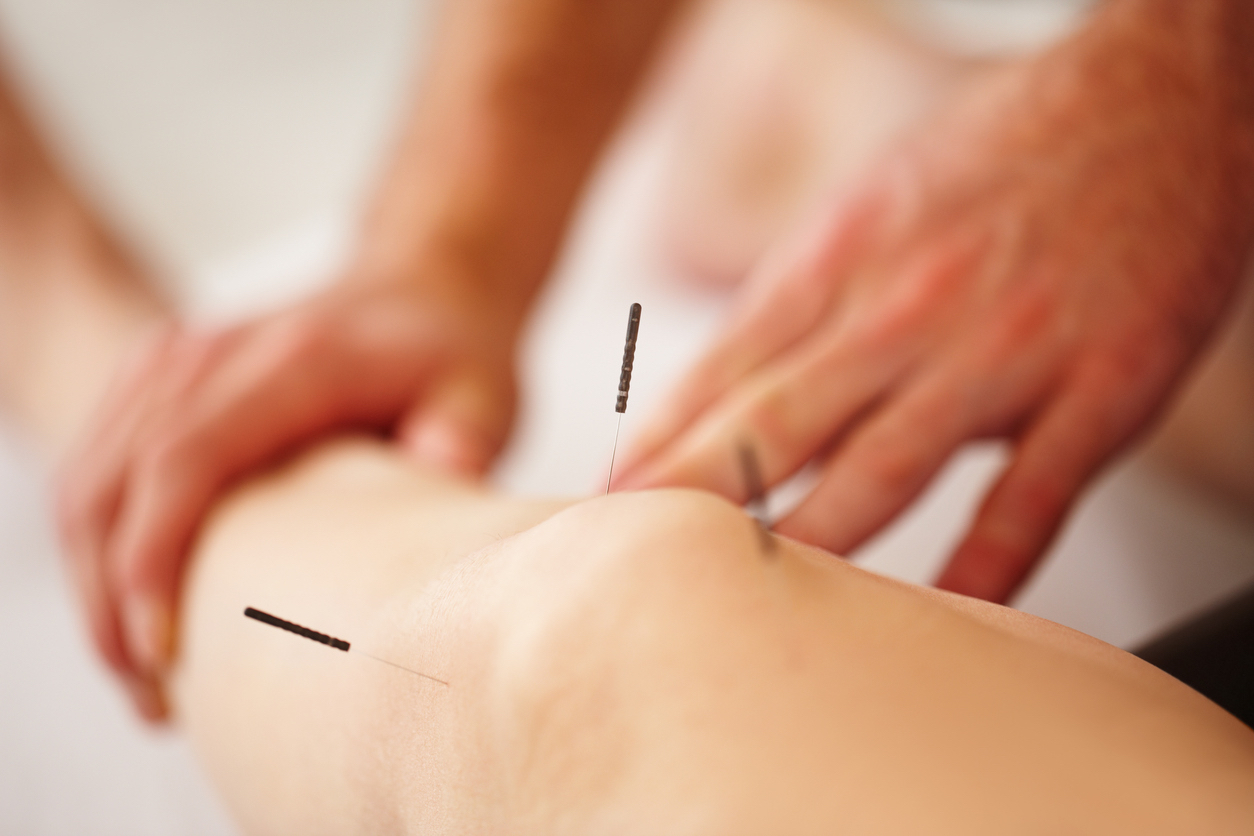
Non-Traditional Treatment Methods
Osteoarthritis is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While conventional treatment methods such as medication, physical therapy, and exercise programs can help reduce pain and inflammation, some individuals may explore non-traditional treatments to improve their symptoms. Here are two non-traditional treatments that have shown potential for managing osteoarthritis:
Acupuncture and its benefits
Acupuncture is an ancient Chinese practice that involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. It is believed to stimulate the body's natural healing abilities and promote physical and emotional wellbeing. While there is limited research on the effectiveness of acupuncture for osteoarthritis, some studies have shown that it can reduce pain and improve joint function. Acupuncture may be particularly effective for individuals who are unable to take medication or have had limited success with conventional treatment methods.
Chiropractic care and its role in Osteoarthritis treatment
Chiropractic care is a complementary therapy that focuses on the musculoskeletal system, particularly the spine. It involves manual manipulation of the spine and other joints to improve joint mobility, reduce pain, and increase range of motion. While there is limited research on the effectiveness of chiropractic care for osteoarthritis, some studies have shown that it can reduce pain and improve joint function. Chiropractic care may be particularly effective for individuals with osteoarthritis of the spine, hips, or knees.
In summary, while conventional treatment methods remain the primary mode of managing osteoarthritis, non-traditional treatments such as acupuncture and chiropractic care may provide additional benefits for some individuals. As with any type of treatment, it is essential to speak with a healthcare professional before exploring non-traditional treatments for osteoarthritis.

Non-Traditional Treatment Methods
Millions of people worldwide suffer from osteoarthritis, a chronic condition that can be managed through conventional treatment methods such as medication, exercise, and physical therapy. However, some individuals opt for non-traditional treatment methods to alleviate their symptoms. Two such methods are acupuncture and chiropractic care.
Acupuncture and its benefits
Acupuncture is an ancient Chinese healing practice that involves inserting thin needles into specific points of the body to stimulate healing and promote overall wellbeing. Limited research has been conducted on its effectiveness for osteoarthritis, but some studies have shown that acupuncture can help alleviate joint pain and improve function. It may be a viable option for individuals who are unable to take medication or have had limited success with conventional treatments.
Chiropractic care and its role in Osteoarthritis treatment
Chiropractic care focuses on improving musculoskeletal function, particularly through manual manipulation of the spine and joints. While limited research has been conducted on its effectiveness for osteoarthritis, some studies have suggested that it can help reduce pain and improve joint function. It may be a particularly effective treatment option for osteoarthritis of the spine, hips, or knees.
Surgical Options
While non-traditional treatments may provide symptom relief, sometimes surgical intervention is necessary to manage osteoarthritis. Two surgical options are joint replacement surgery and arthroscopy.
Joint replacement surgery and its success rate
Joint replacement surgery involves removing damaged parts of a joint and replacing them with a prosthesis. It is typically reserved for individuals with moderate to severe osteoarthritis who have not found relief through conservative treatment methods. Joint replacement surgery has a high success rate, with many individuals experiencing significant pain relief and improved mobility following the procedure.
Arthroscopy and its limitations
Arthroscopy involves using a tiny camera and tools inserted through small incisions to remove damaged tissue from a joint. It is typically reserved for individuals with early-stage osteoarthritis who have not found relief through conservative treatments. While arthroscopy can provide functional improvements, it does not always provide permanent pain relief and may not be suitable for all individuals.
It is essential to discuss all treatment options with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action for managing osteoarthritis for each individual.

