Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It results in pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility of the affected joint, which can have a huge impact on a person's quality of life. This blog will explore osteoarthritis and the importance of awareness about this condition.

Osteoarthritis is a condition where the protective cartilage that covers the ends of bones wears down over time. This causes the bones to rub against each other, leading to pain, swelling and stiffness in the joint. It commonly affects the hands, hips, knees, and spine. The prevalence of osteoarthritis is increasing worldwide and is expected to be one of the leading causes of disability in the coming years. It is estimated that over 30 million people in the United States have osteoarthritis, and this number is expected to reach 78 million by the year 2040.
Why is awareness about Osteoarthritis important?
Awareness about osteoarthritis is important for several reasons. Firstly, it can help people recognize the symptoms of the condition and seek medical help early. Early intervention can help slow the progression of the disease and improve outcomes for the patient. Secondly, awareness can help reduce the stigma associated with the condition. Many people with osteoarthritis face discrimination and misunderstanding from their peers, which can exacerbate feelings of isolation and depression.
Overall, osteoarthritis is a debilitating condition that requires greater attention and awareness. By educating ourselves and others about this condition, we can help improve outcomes for patients and reduce the stigma associated with this condition.
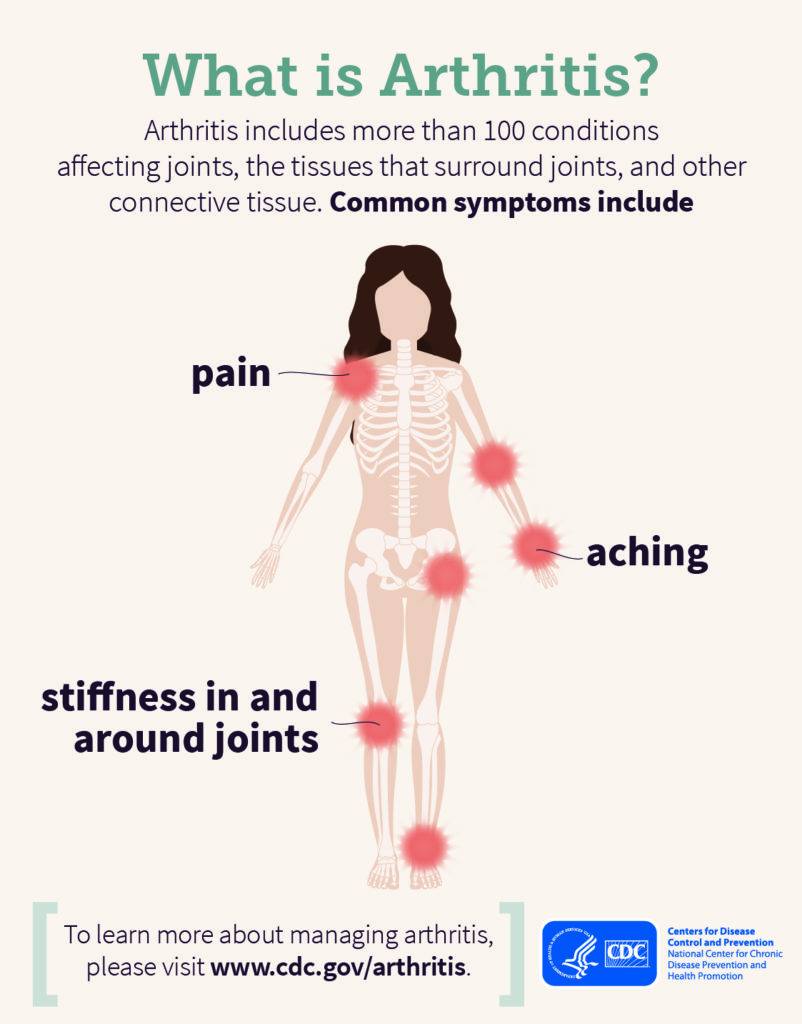
Understanding Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the protective cartilage that covers the ends of bones deteriorates over time, causing bones within the joint to rub against each other. This leads to pain, swelling, stiffness, and decreased mobility in the affected joint.
Causes and risk factors of Osteoarthritis
There are several factors that can increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis, including age, gender, genetics, and lifestyle factors such as obesity and physical inactivity. People who have had joint injuries or those with joint deformities or other medical conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis are also more likely to develop osteoarthritis.
Symptoms of Osteoarthritis
Symptoms of osteoarthritis often develop gradually and worsen over time. Common symptoms include pain, stiffness, swelling, and a decreased range of motion in the affected joint. In some cases, people with osteoarthritis may also experience a crunching or grinding sensation in the joint when moving. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms to receive early intervention and improve outcomes for the patient.
Awareness about osteoarthritis is essential for recognizing the symptoms and seeking medical attention early. Early intervention can help slow the progression of the disease and improve outcomes for patients. Additionally, awareness can help reduce the discrimination and misunderstandings that individuals with osteoarthritis may face, which can exacerbate feelings of isolation and depression. Overall, osteoarthritis is a debilitating condition that requires greater attention and awareness. Educating ourselves and others about this condition is crucial to helping individuals manage their condition.

Diagnosis and Treatment
How is Osteoarthritis diagnosed?
Osteoarthritis is typically diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI. During the physical examination, the doctor will evaluate the affected joint for signs of tenderness, swelling, redness, and range of motion. They will also ask questions about the patient's symptoms, medical history, and family history.
Imaging tests can help confirm the diagnosis and provide more information about the severity of the disease. X-rays may show changes in the joint, such as bone spurs or a reduction in the space between bones, while an MRI can show details of the soft tissues, such as cartilage and ligaments.
Pain management and treatment options
There are several options for managing the pain associated with osteoarthritis. Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce pain and swelling. In some cases, prescription-strength medications may be necessary.
Patients may also benefit from physical therapy, which can help strengthen the muscles around the affected joint, improve flexibility, and reduce pain. In severe cases, joint replacement surgery may be necessary.
Changes to lifestyle factors such as maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular exercise, and avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms can also help manage osteoarthritis symptoms.
In conclusion, osteoarthritis is a common joint disease that can cause significant pain and disability. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing symptoms and improving outcomes for patients. Through a combination of medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes, patients can effectively manage the pain associated with osteoarthritis and improve their quality of life.

Lifestyle Changes
Exercises and Physical Therapy for Managing Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is commonly managed with physical therapy. The aim of physical therapy is to strengthen the muscles surrounding the affected joint, enhance flexibility, and decrease pain. Exercise programs for patients with osteoarthritis include low-impact training, stretching, and resistance training. Low-impact exercise, such as swimming, walking, and cycling, particularly in water, can help to reduce pain and stiffness. Resistance training can also help build muscle strength, which aids in supporting the joint.
Dietary Modifications and Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight can help to reduce the load on joints, reducing the symptoms associated with osteoarthritis. Losing weight through dietary modifications such as reducing processed foods and increasing fruits and vegetables has been linked with a decrease in symptoms of osteoarthritis. Additionally, there is evidence supporting the use of omega-3 fatty acids, found in foods such as fish, olive oil, avocado, and nuts, to decrease inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
In conclusion, lifestyle modifications such as physical therapy and dietary changes can be effective in managing the symptoms of osteoarthritis. Maintaining a healthy weight, reducing processed foods, and increasing the consumption of fruits and vegetables, as well as incorporating low-impact physical exercises, can improve a patient's quality of life. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most effective combination of therapies to manage the symptoms of osteoarthritis effectively.

Coping with Osteoarthritis
Exercises and Physical Therapy for Managing Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis can be managed with physical therapy that aims to strengthen the muscles around the affected joint, enhance flexibility, and reduce pain. Low-impact exercises such as swimming, walking, and cycling, especially in water, can help reduce pain and stiffness. Resistance training can also help build muscle strength, which aids in supporting the joint.
Dietary Modifications and Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight helps reduce the load on joints and the symptoms associated with osteoarthritis. Dietary modifications such as reducing processed foods and increasing fruits and vegetables have been linked with a decrease in osteoarthritis symptoms. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in foods such as fish, olive oil, avocado, and nuts, can decrease inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
Mental and emotional health of Osteoarthritis patients
Living with osteoarthritis can take a toll on the mental and emotional well-being of patients, with feelings of depression, anxiety, and frustration being common. To manage these emotions, patients can talk to a counselor or mental health professional, practice relaxation techniques, and pursue hobbies or activities that bring joy and fulfillment.
Support groups and resources available
Support groups provide a community of people going through similar experiences and can offer practical advice, emotional support, and encouragement. There are also numerous online resources available, such as forums, chat rooms, and educational materials, that can help patients stay informed and connected.
In conclusion, while osteoarthritis can be a challenging condition to manage, there are various lifestyle modifications, physical therapies, and emotional support resources available. Patients should consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most effective combination of therapies to manage their symptoms.

